Bronchoscopy
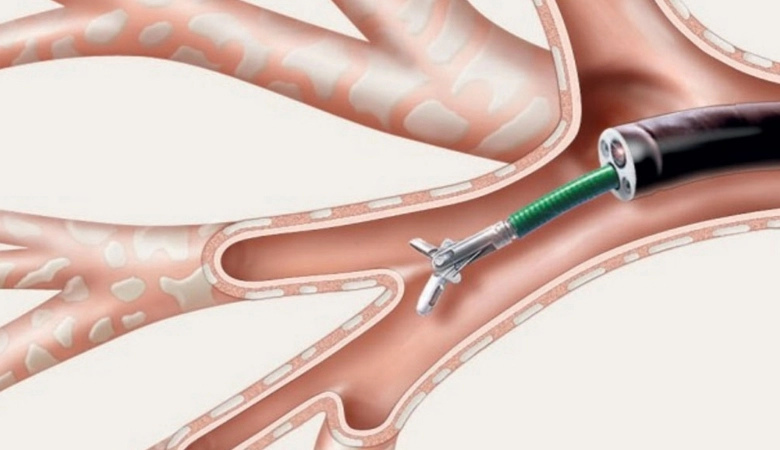 Bronchoscopy is a common diagnostic procedure in which the doctor examines the inner surfaces of the patient's trachea and bronchi. The respiratory system is visualised using a fibro bronchoscope: a flexible fibre-optic cable enclosed in a protective braid. This tool is equipped with a camera, a light source and a manipulator.
Bronchoscopy is a common diagnostic procedure in which the doctor examines the inner surfaces of the patient's trachea and bronchi. The respiratory system is visualised using a fibro bronchoscope: a flexible fibre-optic cable enclosed in a protective braid. This tool is equipped with a camera, a light source and a manipulator.
Patients are sent for a lung bronchoscopy by their general practitioner or pulmonologist. Doctors determine the indications for the study and formulate a preliminary diagnosis, which must be confirmed through the use of a fibro bronchoscope.
Assignment of the procedure
Indications for bronchoscopy are:
- darkening of the lungs detected during an X-ray;
- signs of cancerous abnormalities of the respiratory system;
- confirmed presence of a foreign body in the lungs;
- systematic dyspnoea without chronic lung damage.
Pulmonary abscesses and cysts detected by radiographs may be additional reasons for referring patients for this investigation. This procedure is prescribed for adults and children who have experienced systematic hemoptysis, complicated pneumonia, bronchial asthma or abnormal narrowing of the bronchial lumen.
Bronchoscopy is optionally used against the previously diagnosed pathologies of the upper or lower respiratory tract. Doctors systematically monitor the progress made as a result of conservative or surgical treatment.
Restrictions on diagnostic manipulations
Contraindications for bronchoscopy are divided into two groups - absolute and relative. Pulmonologists include in the first group:
- second- and third-degree stenoses of the larynx or trachea;
- third-degree respiratory failure;
- exacerbation of bronchial asthma.
When performing diagnostic manipulations against these pathologies, irreversible damage to the bronchi on the surface of the fibro bronchoscope is possible. Current clinical trial protocols suggest that bronchoscopy should not be performed if a patient has been diagnosed with an aortic aneurysm, has had a heart attack or stroke less than six months ago.
Similar prohibitions are imposed on endoscopic manipulations in the case of people with blood clotting disorders or individual intolerance to anaesthetic drugs. An acute allergic reaction can lead to the development of anaphylactic shock.
Relative contraindications that do not lead to complications during bronchoscopy are:
- acute viral and bacterial infections;
- menstrual bleeding;
- acute attacks of chronic asthma;
- second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
Patients with these restrictions are referred for an imaging examination of the trachea and bronchi by a general practitioner or pulmonologist. In emergency cases, doctors have to neglect possible complications after bronchoscopy on the background of a critical condition.
Our doctors

Bronchoscopy at JSC "Medicina" (Academician Roytberg Clinic)
JSC "Medicina" (Academician Roytberg Clinic) is located in the centre of Moscow. The specialists in the diagnostic department of the clinic have extensive experience in performing bronchoscopy on patients of all ages. Advantages of our clinic are:
- high-precision diagnostic and therapeutic equipment;
- cooperation with the largest medical centres in the world;
- qualified doctors and staff;
- possibility of receiving diagnostic services as part of the VMI system.
Cooperation of the clinic of Academician Roytberg with the leading operators of voluntary medical insurance programs makes it possible to provide full payment for bronchoscopy by insurance companies. Patients only have to choose a suitable day to visit the clinic. The price of lung bronchoscopy depends on the scope of the upcoming examination and the equipment used.
Preparatory measures
Preparation of any patient for bronchoscopy includes a number of diagnostic procedures:
- X-ray examination of the lungs;
- electrocardiogram;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- blood clotting analysis.
The data obtained during these manipulations will help doctors to assess the degree of risk during an endoscopic examination of the patient's trachea and bronchi. A child or adult should take mild sedatives the night before their visit to the clinic. Eating is allowed 8-10 hours before the procedure. Smoking patients should refrain from using tobacco products. Bronchoscopy is performed on an empty stomach. On the morning of the day of the examination a series of purgative enemas should be performed.
Diagnostic examination process
All manipulations do not exceed 40 minutes. The patient receives bronchodilators and painkillers in the form of subcutaneous injections or aerosols. The patient should then take the position indicated by the doctor, either lying on his/her back or sitting. The bronchoscope is inserted through the oral cavity or one of the patient's nasal passages. As the pulmonologist progresses to the lower parts of the respiratory system, he/she can observe the inner surfaces of the trachea, vocal slit and bronchi. After all diagnostic procedures are completed, the bronchoscope is slowly removed. The patient is sent to the hospital under the supervision of clinic staff - timely medical care will avoid the development of severe complications.
Diagnostic side effects
After the diagnostic manipulations are completed, patients may feel nasal congestion and complain about the presence of a lump in the throat. During the next two hours it is not recommended to smoke and eat solid food. Motorists should refrain from driving as painkillers can reduce reaction speed.
In rare cases, other side-effects may occur after bronchoscopy:
- hemoptysis;
- chest pain;
- wheezing when breathing;
- episodes of nausea;
- increased body temperature.
If these symptoms are detected, a doctor should be seen immediately. Such symptoms may indicate a pneumothorax, pneumonia or an acute allergic reaction.




